From the Blog
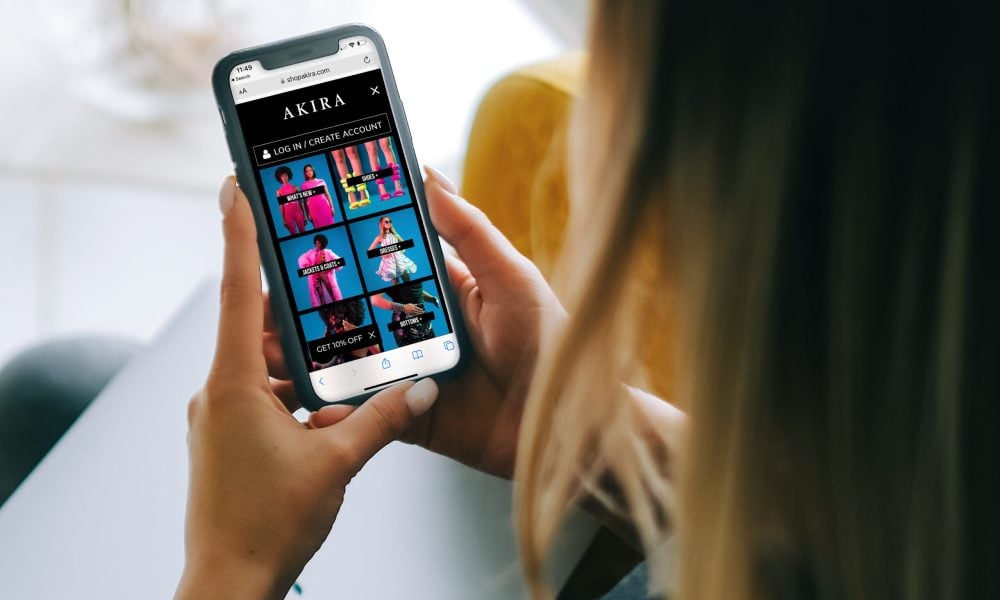
7 Hacks to Optimize Magento Payment Processing
Online shopping is at an all-time high and consumers are looking to spend their money with eCommerce businesses they trust. This means there’s no better time for Magento users to optimize their payment processing systems than right now.